In the era of cloud computing, where businesses increasingly rely on cloud services to store and process their data, security has become a paramount concern. The shared responsibility model is a foundational concept in cloud security that outlines the division of security responsibilities between cloud service providers (CSPs) and their customers. This model defines who is responsible for securing various components of the cloud infrastructure, applications, and data. In this article, we will delve into the shared responsibility model, its significance in cloud security, its application in different cloud service models, and best practices for navigating this collaborative approach to safeguarding digital assets.
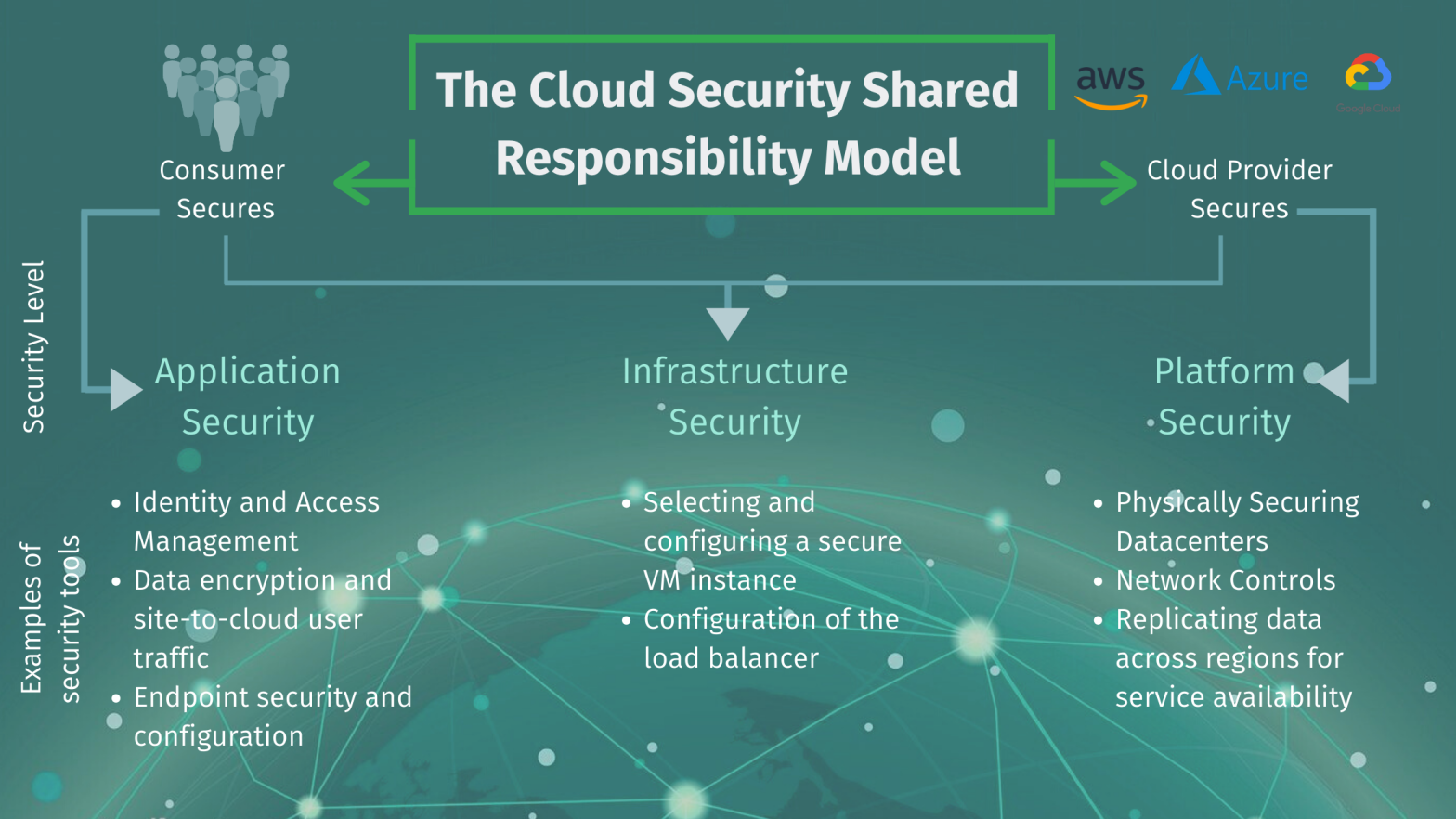
Understanding the Shared Responsibility Model: The shared responsibility model is a framework that clarifies the security responsibilities of both cloud service providers and their customers. It outlines which security tasks each party is accountable for, ensuring that there is no ambiguity regarding security responsibilities within the cloud environment.
In essence, the model divides security responsibilities into two main categories:
- Provider Responsibilities: Cloud service providers are responsible for securing the underlying cloud infrastructure, including physical facilities, networking, and the hypervisor layer. They also provide security controls, such as firewalls, intrusion detection, and encryption mechanisms, to protect the infrastructure.
- Customer Responsibilities: Customers are responsible for securing their applications, data, and operating systems that they deploy on the cloud infrastructure. This includes configuring security settings, managing access controls, and implementing encryption for their data.
Significance of the Shared Responsibility Model: The shared responsibility model is essential for several reasons:
- Clarity: The model eliminates confusion by clearly defining which security aspects are managed by the cloud provider and which fall under the customer’s purview.
- Collaboration: It fosters collaboration between CSPs and customers in managing security risks, ensuring that both parties work together to create a secure environment.
- Adaptability: The model is flexible and applicable to various cloud deployment models, including Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS), Platform as a Service (PaaS), and Software as a Service (SaaS).
- Compliance: By defining security roles, the shared responsibility model helps organizations meet regulatory requirements and industry standards.
Application of the Shared Responsibility Model in Different Cloud Service Models:
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service): In an IaaS environment, the cloud provider manages the core infrastructure, including virtualization, networking, and storage. Customers are responsible for securing their operating systems, applications, and data. They must configure firewalls, implement security patches, and manage access controls within the virtual machines they deploy.
- PaaS (Platform as a Service): In a PaaS environment, the cloud provider manages not only the infrastructure but also the underlying application platform. This includes the runtime environment, databases, and development frameworks. Customers are responsible for securing their applications and data within the PaaS platform.
- SaaS (Software as a Service): In a SaaS environment, the cloud provider takes care of the entire application, including the infrastructure, platform, and software. Customers primarily focus on configuring user access and permissions to the SaaS application and managing their own data within the application.
Best Practices for Navigating the Shared Responsibility Model:
- Understand the Model: Clearly comprehend the shared responsibility model in the context of your chosen cloud service model. Familiarize yourself with the specific responsibilities allocated to the CSP and your organization.
- Collaborate with Your CSP: Engage with your cloud provider to understand their security measures, certifications, and compliance with relevant standards. Discuss how they protect the underlying infrastructure.
- Assess Risks: Conduct a comprehensive risk assessment to identify potential security vulnerabilities and threats within your applications and data. Tailor your security measures to address these risks.
- Implement Security Controls: Apply appropriate security controls, such as encryption, multi-factor authentication, intrusion detection, and intrusion prevention systems. These measures enhance the security of your assets within the cloud environment.
- Regular Audits and Monitoring: Continuously monitor your cloud environment for security incidents, anomalies, and unauthorized activities. Conduct regular security audits to ensure compliance with your organization’s security policies.
- User Access Management: Manage user access and permissions diligently. Implement the principle of least privilege, ensuring that users have only the access they need to perform their roles.
- Patch Management: Keep your operating systems, applications, and software up to date with the latest security patches. Regularly apply updates to address known vulnerabilities.
- Data Protection: Implement encryption for sensitive data both at rest and in transit. This safeguards your data from unauthorized access and breaches.
- Disaster Recovery: Develop a robust disaster recovery plan to ensure business continuity in the event of data loss or system outages. Regularly test your recovery processes.
- Education and Training: Train your employees on cloud security best practices. Educate them about the shared responsibility model and their role in maintaining a secure cloud environment.
The shared responsibility model forms the bedrock of cloud security, enabling cloud service providers and their customers to collaboratively manage security risks and protect digital assets. By clearly defining the division of security responsibilities, this model ensures transparency, collaboration, and alignment in safeguarding cloud environments. Organizations must take ownership of their applications, data, and configurations while leveraging the security measures provided by their cloud providers. By adhering to best practices and effectively navigating the shared responsibility model, businesses can harness the benefits of cloud computing without compromising on security.